PEOPLE

FROM DETECTORS TO DARK MATTER: EUROPE REWARDS RESEARCH WITH PARTICLE ACCELERATORS
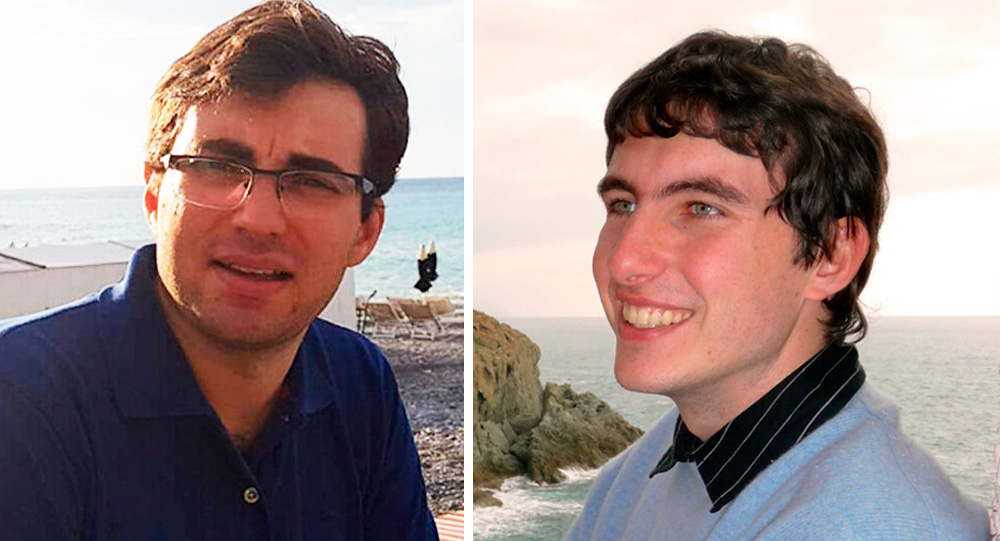
Interview with Lorenzo Bianchini, researcher of the INFN Pisa division, and Andrea Celentano, researcher of the INFN Genoa division, respectively winners in 2020 of an ERC Consolidator Grant and an ERC Starting Grant, for a total funding of over three million euros
ASYMOW and POKER are the names of the two INFN projects awarded in 2020 by the European Research Council (ERC) for their innovative character and for the merit of their applicants: Lorenzo Bianchini, a researcher at the INFN Pisa division, and Andrea Celentano, a researcher at the INFN Genoa division. The goal of the two projects is to develop innovative techniques for analysing data obtained from LHC accelerator collisions and to study light dark matter.
The idea on which the ERC Grants are based is to finance innovative research projects following a bottom-up approach, involving researchers of any nationality and age, who are at the start of their careers or are intending to pursue their research paths by developing unconventional methods. The ERC Consolidator Grant, in particular, is awarded to excellent researchers with at least seven and up to twelve years of post-doctorate experience. In the 2020 funding round, Lorenzo Bianchini was awarded 1,683,750 euros for the project ASYMOW power to the LHC data - an ASYmptotically MOdel-independent measurement of the W boson mass. The project’s main goal is to develop a new methodology for analysing data and calibration techniques for the CMS detector, one of the four big experiments of CERN’s LHC that, alongside ATLAS, enabled the discovery of the Higgs boson.
Devised to incentivise the initial phase of excellent researchers’ careers, and intended for researchers with 2-7 years of post-doc experience, the ERC Starting Grant 2020 awarded Andrea Celentano almost 1.5 million euros in funding for the POKER project (POsitron resonant annihilation into darK mattER). This project is dedicated to researching a particular type of dark matter: light dark matter.
We asked Lorenzo Bianchini and Andrea Celentano to explain the investment strategy for the grant that was awarded to them, as well as the aims and development prospects for their research projects.
...
NEWS
TECHNOLOGICAL RESEARCH
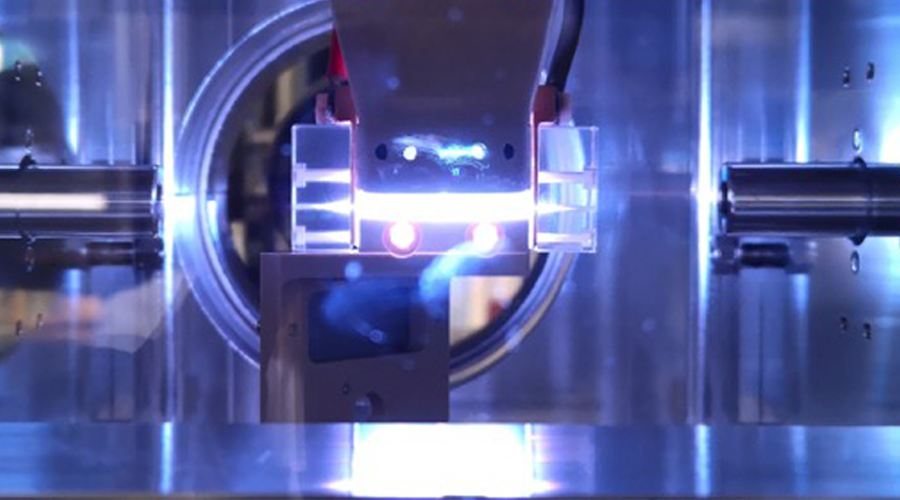
HIGH-QUALITY ELECTRONS ACCELERATED WITH PLASMA AT SPARC_LAB
One of the factors that most limits the application of plasma accelerators is the energy spread that the beam accumulates during acceleration in the plasma module. Recently, an experiment conducted by researchers of the SPARC_LAB group at the INFN Frascati National Laboratories demonstrated, for the first time, that it’s possible to solve this problem and thus accelerate a beam of high-quality electrons ...

RESEARCH INFRUSTRUCTURES
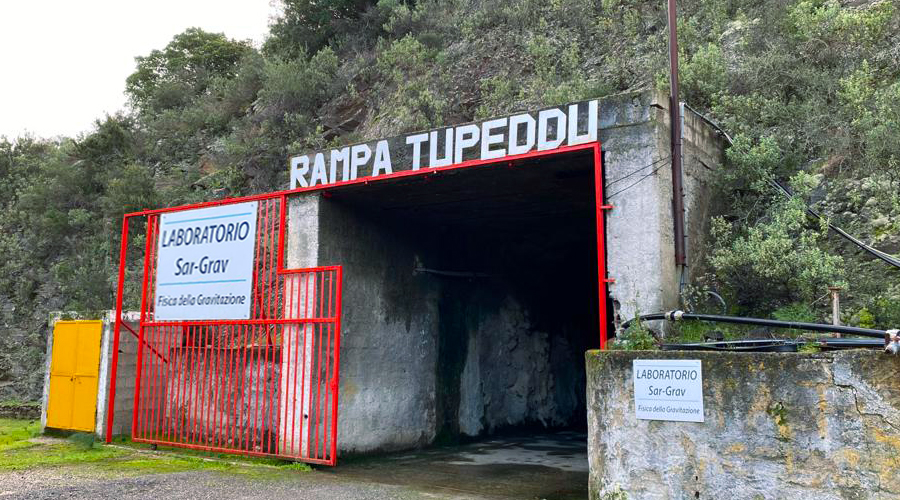
THE EINSTEIN TELESCOPE - THE GEOPHYSICAL SURVEYING CAMPAIGN TAKES OFF
In Sardinia, the installation of the first network of seismic sensors on a large scale has begun for an extensive geophysical surveying campaign near the Sos Enattos metal mine, in Lula, the site Italy put forward to host the Einstein Telescope (ET). The ET is the observatory for third-generation gravitational waves, to which INFN, the Italian National Institute for Geophysics and Volcanology (INGV), and the National Institute for Astrophysics (INAF), and the Universities of Sassari and Cagliari are contributing. ...

APPLICATIONS
AN INNOVATIVE PROTOCOL FOR DISCOVERING POTENTIAL NEW DRUGS
An innovative protocol for discovering potential new drugs has been developed by a broad, international team led by researchers from INFN, the University of Trento, the University of Perugia, the Dulbecco Telethon Institute, the Telethon Foundation. The Pharmacological Protein Inactivation by Folding Intermediate Targeting (PPI-FIT) protocol consists in identifying small molecules that can block ...
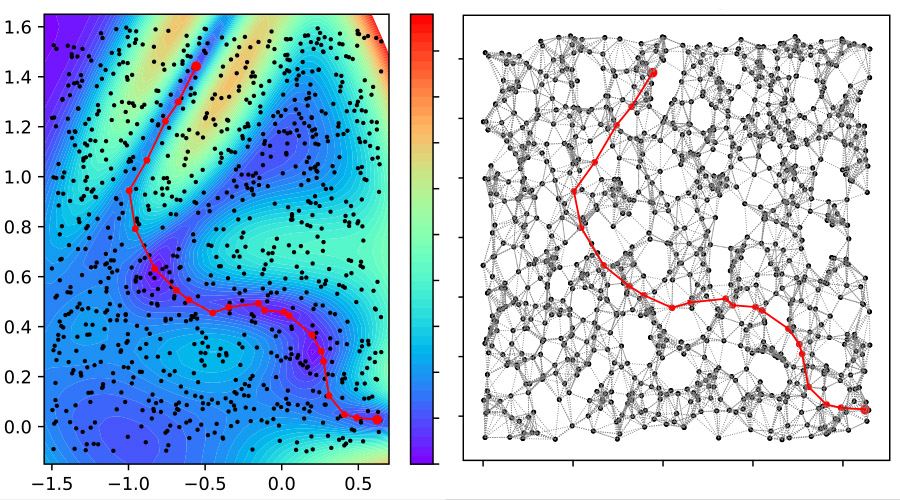
APPLICATIONS
A QUANTUM ALGORITHM FOR SIMULATING THE TRANSFORMATIONS OF PROTEINS
A study conducted by three theoretical physicists of the University of Trento, which appeared yesterday in the Physical Review Letters, demonstrates the validity and the potential for an approach founded on the use of quantum computing in simulating structural changes to which proteins are subjected in the course of their lives, biological transformations on which the synthesis and activation of the ...

RESEARCH
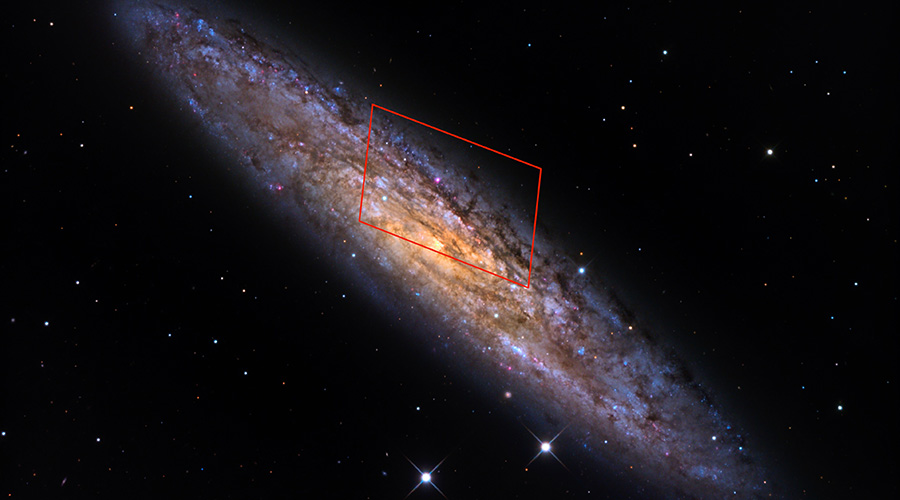
THE FERMI SPACE TELESCOPE OBSERVES THE FIRST ERUPTION OF AN EXTRAGALACTIC MAGNETAR
Three studies published in Nature, Nature Astronomy, and The Astrophysical Journal Letters throw light on the origin of some Gamma Ray Bursts (GRB). Analysing the data obtained by European and American space probes following the detection of a GRB on 15 April 2020, the three studies trace the event back to the eruption of a magnetar: a neutron star with a very intense magnetic field, positioned in ...
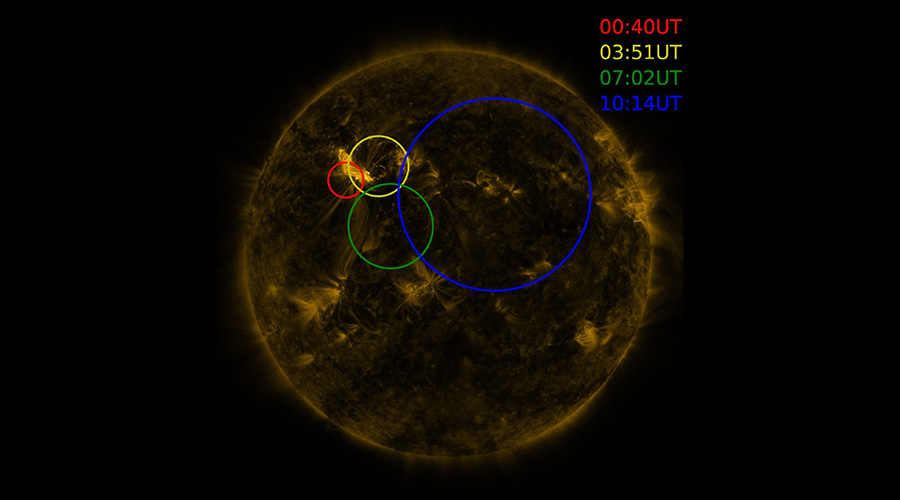
RESEARCH
THE FIRST CATALOGUE OF SOLAR FLARES OBSERVED IN THE GAMMA FREQUENCY
A first, detailed, and extensive catalogue of solar flares - violent explosions of electromagnetic radiation that take place in the sun’s corona - has been presented in the journal Astrophysical Journal Letter Supplement (APJS). These solar flares were observed in the period from 2010 to 2018 in the gamma frequency by the Large Area Telescope (LAT), one of the two detectors installed onboard NASA’s ...
FOCUS
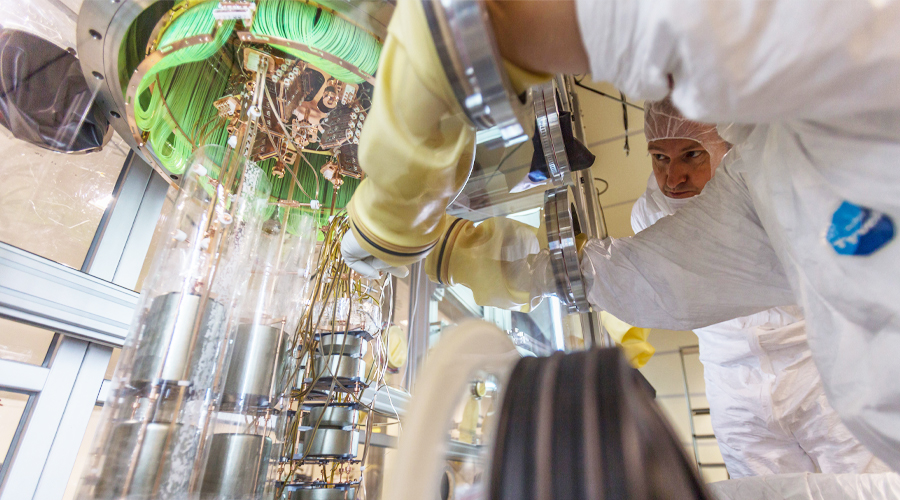 GERDA PAVES THE WAY FOR LEGEND
GERDA PAVES THE WAY FOR LEGEND
Neutrinos are essential particles for understanding nature. Unfortunately, since they interact very little with matter, they are extremely evasive and it is, therefore, necessary to confront ever new technological challenges to be able to study them in depth. These are decisive scientific undertakings because understanding nature in detail would lead to a turning point in our knowledge. In particular, the study of an extremely rare, hypothetical process, which has still never been observed, called double beta decay without neutrino emission, would make it possible to understand whether the neutrino is a Majorana particle, or if it coincides with its antiparticle. The GERDA (GERmanium Detector Array) experiment, at INFN Gran Sasso National Laboratories (LNGS), has investigated this process, using a technology based on Germanium crystals enriched from the germanium-76 Isotope. ...
INFORMATION AND CONTACT
Images cover
GERDA at Gran Sasso National Laboratories, © INFN
Download the newsletter in pdf format
ENGLISH VERSION | ITALIAN VERSION
INFN - COMMUNICATIONS OFFICE
comunicazione@presid.infn.it
+39 06 6868162
EDITORIAL BOARD
Coordination:
Francesca Scianitti
Project and contents:
Eleonora Cossi, Matteo Massicci, Anna Greco, Francesca Mazzotta, Francesca Scianitti, Antonella Varaschin
Graphic design:
Francesca Cuicchio
Translation
ALLtrad
ICT service:
Servizio Infrastrutture e Servizi Informatici Nazionali INFN