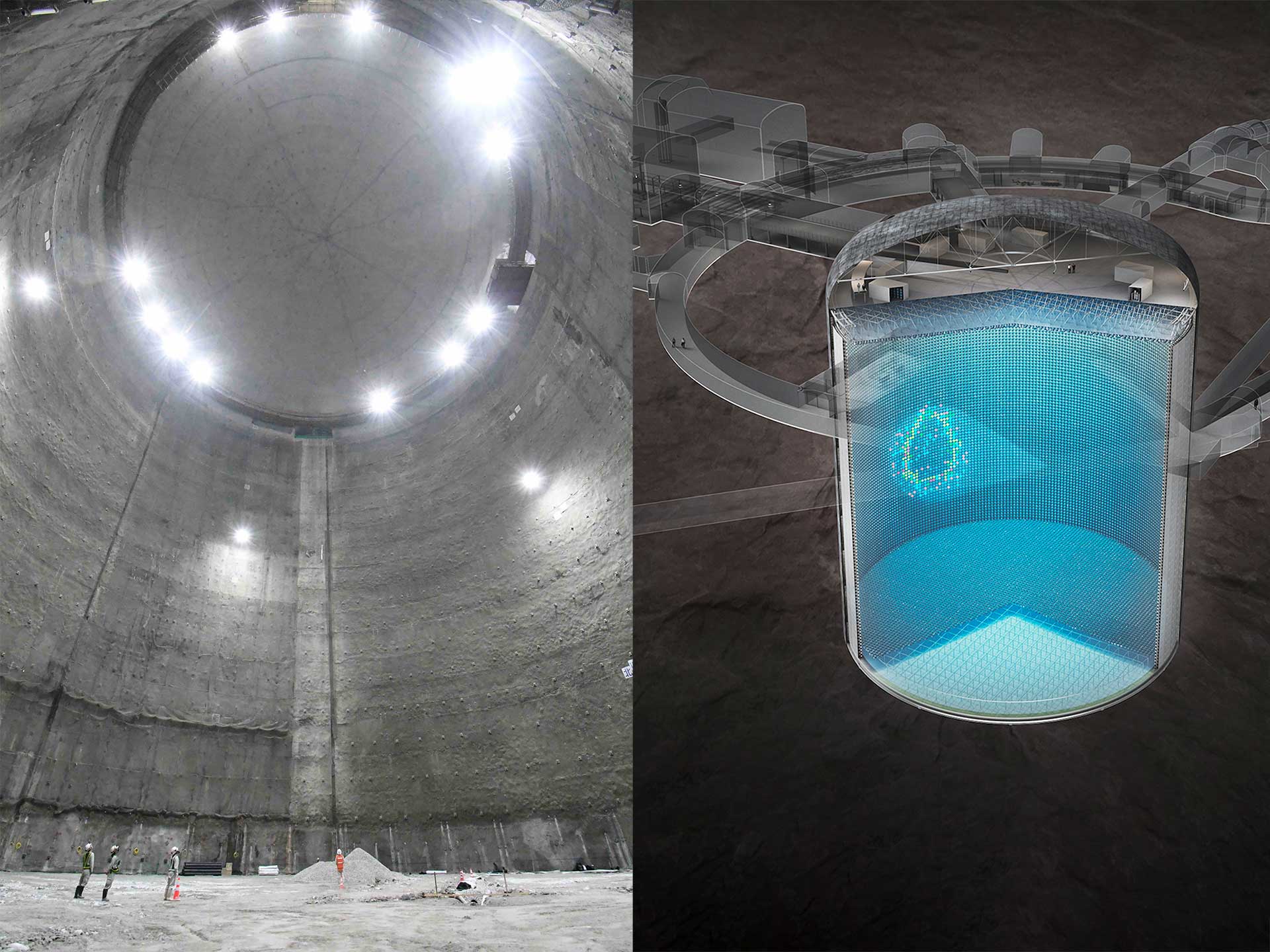
The European Research Council (ERC) has assigned to Gabriele Rosi, researcher of the Florence division of the INFN an ERC Starting Grant 2018 of € 1,550 million for a research project on gravitational physics. This is the development of the five-year project MEGANTE (MEASuring the Gravitational constant with Atom interferometry for Novel fundamental physics TEsts) which consists in the realization of a new experimental apparatus dedicated to the measurement of the gravitational constant. The new apparatus will have a higher sensitivity than the existing ones and will be realized using quantum technologies such as atomic interferometry. “The measurement of the gravitational constant is considered in the metrological field the most difficult to achieve and, in fact, is the fundamental constant known with the greatest uncertainty” comments Gabriele Rosi, researcher of the Florence section of INFN. Many research groups, using “classic” methods such as pendulums and torsion balances, are trying to push the relative accuracy to 10 parts per million (ppm) “concludes Rosi. The idea of the MEGANTE project stems from the experience gained during the MAGIA experiment of INFN and the European Non-Linear Spectroscopy Laboratory (Lens) of the University of Florence, which has directly measured, for the first time in the world, the curvature of the gravitational field. MAGIA which uses atoms in free fall instead of measuring probes of macroscopic mechanical objects, has reached a remarkable accuracy, but it will be MEGANTE to try the qualitative leap.
The European Research Council (ERC) has assigned to Gabriele Rosi, researcher of the Florence division of the INFN an ERC Starting Grant 2018 of € 1,550 million for a research project on gravitational physics. This is the development of the five-year project MEGANTE (MEASuring the Gravitational constant with Atom interferometry for Novel fundamental physics TEsts) which consists in the realization of a new experimental apparatus dedicated to the measurement of the gravitational constant. The new apparatus will have a higher sensitivity than the existing ones and will be realized using quantum technologies such as atomic interferometry. “The measurement of the gravitational constant is considered in the metrological field the most difficult to achieve and, in fact, is the fundamental constant known with the greatest uncertainty” comments Gabriele Rosi, researcher of the Florence section of INFN. Many research groups, using “classic” methods such as pendulums and torsion balances, are trying to push the relative accuracy to 10 parts per million (ppm) “concludes Rosi. The idea of the MEGANTE project stems from the experience gained during the MAGIA experiment of INFN and the European Non-Linear Spectroscopy Laboratory (Lens) of the University of Florence, which has directly measured, for the first time in the world, the curvature of the gravitational field. MAGIA which uses atoms in free fall instead of measuring probes of macroscopic mechanical objects, has reached a remarkable accuracy, but it will be MEGANTE to try the qualitative leap.
31 July 2018